Climate change drives an increase in vultures, leaving cattle ranchers without any safe haven
- U.S. cattle farmers face growing threats from northward-migrating black vultures, protected under the Migratory Bird Treaty Act, which attack calves and disrupt operations. - Climate change and human activity enable vultures to thrive in colder regions, exploiting roadkill, farms, and suburban sprawl for reliable food sources. - Farmers employ non-lethal deterrents like adjusted calving schedules and vulture effigies, but legal protections limit population control options. - Experts warn of escalating hu
American cattle ranchers are facing a growing challenge from black vultures, a federally protected species that is rapidly moving northward as a result of climate change and human expansion. Previously limited to the southeastern United States and parts of Latin America, these birds are now attacking young livestock and interfering with farm routines, leaving ranchers struggling to cope. Andrew Farnsworth, a visiting researcher at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, noted that milder winters and shifting habitats have allowed black vultures to flourish in areas that were once inhospitable. "They excel at locating food and remembering those locations," he explained, pointing out that roadkill, cattle operations, and suburban growth have all boosted their food supply, according to
The fact that black vultures do not migrate seasonally makes the issue worse. Unlike many birds that travel with the seasons, black vultures settle and breed in new areas, establishing permanent populations. This has left ranchers like Tom Karr from Pomeroy, Ohio, with no escape. Ten years ago, Karr lost a calf to vultures and changed his calving season to later in the year, only to discover the birds stayed all year long. "They basically eat them alive," Karr said, describing the persistent threat. Joanie Grimes, who farms in Hillsboro, Ohio, has also changed her approach, keeping newborn calves close to barns for several days to reduce risk. "We've been dealing with these birds for 15 years, but keeping calves out of distant fields has made a difference," she told the AP.
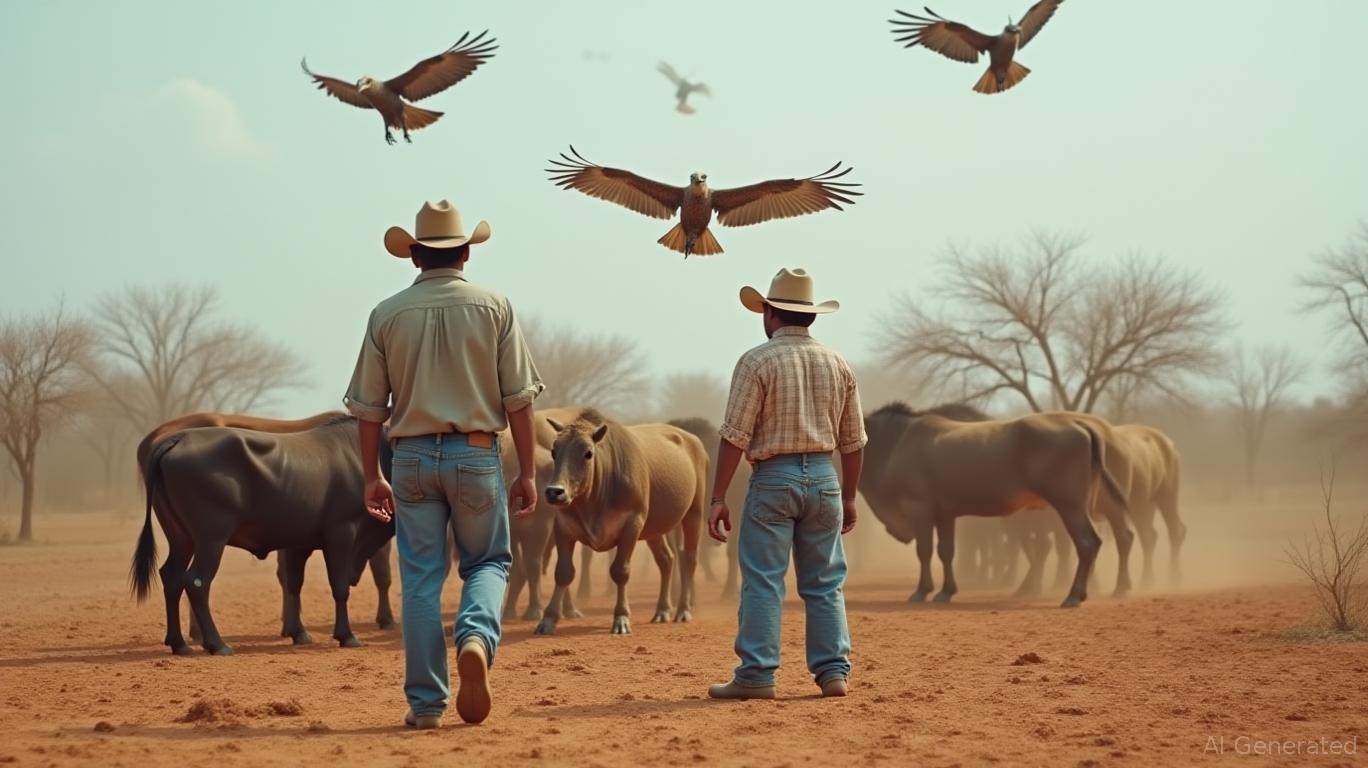

The northward spread of black vultures is closely linked to larger environmental changes. Milder winters caused by climate change have enabled these birds to move into northern states. At the same time, human activities have created plentiful food sources, Farnsworth explained. Suburban expansion leads to more roadkill, and predictable cattle birthing seasons offer steady meals. The birds’ intelligence and ability to learn from each other make the problem worse, as groups of vultures share information about where to find food.
To keep the birds at bay, farmers are trying a variety of tactics. Annette Ericksen, who runs Twin Maples Farm in Milton, West Virginia, said she has not lost any animals to vultures but has kept a close eye on them for years. In some places, farmers are experimenting with fake vulture decoys and adjusting grazing patterns. Still, these efforts only provide limited relief. Because black vultures are protected under the Migratory Bird Treaty Act, lethal control is restricted, forcing ranchers to rely on non-lethal deterrents.
This situation underscores the unexpected effects of climate-related ecological changes. As black vultures continue to move north, cattle producers in the U.S. are under increasing pressure to find new ways to coexist. Experts caution that unless broader solutions—such as targeted habitat management or regulatory changes—are implemented, tensions between ranchers and these adaptable birds are likely to grow.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
NEAR's Reduced Inflation: Sensible Adjustment or Weakening of Governance?
- NEAR Protocol slashed annual token inflation to 2.4% from 5%, bypassing a failed community vote and sparking governance debates. - The October 30 upgrade reduces new token issuance by 60 million yearly, lowers staking yields to 4.5%, and prioritizes curbing dilution. - Critics, including staking firm Chorus One, accuse the core team of undermining decentralized governance, as NEAR’s price fell 8% post-announcement. - The move mirrors strategies by Solana and Polkadot but highlights tensions between econo

"Potential for Increased Volatility as Eigen Focuses on Expanding Its Ecosystem Rather Than Token Offerings"
- Eigen Foundation clarifies EIGEN token transfers from treasury are for ecosystem grants, partnerships, and liquidity, not team unlocks or sales. - Market faces $653M+ in token unlocks (Oct-Nov 27), led by SUI ($119M) and EIGEN ($43.8M), raising volatility risks for smaller projects like GRASS and SIGN. - Analysts warn high-unlock projects face sharper price swings, contrasting Eigen's governance stability with broader market uncertainties over liquidity absorption. - Rovaren Token (RVN) introduces AI-pow
Zcash Sets New Standard for Crypto Privacy with $412 Rally and Zero-Knowledge Enhancements
- Zcash (ZEC) surged to a $412 seven-year high, driven by privacy demand, ZK upgrades, and market shifts toward zero-knowledge tech. - ZEC's $6.8B market cap now surpasses Monero and Shiba Inu, fueled by 400% October gains and 4.1M shielded tokens on Orchard protocol. - Electric Coin Co. unveiled Q4 2025 roadmap with Zashi wallet enhancements, P2SH multisig security, and Solana integrations to boost privacy usability. - Analysts highlight Zcash's optional transparency model as a compliance advantage over f

Investors Turn to Blockchain as Meme Coins Struggle During Market Fluctuations
- Meme coins like SPX6900 face waning momentum as investors shift to blockchain projects like NB HASH, which integrates AI and decentralized infrastructure. - Fed Chair Powell's cautious stance on rate cuts (70% December cut probability) dampened tech stocks, while NatWest and SERES Group boosted earnings amid cost-cutting and EV growth. - Leidos and Summit Hotel Properties raised dividends, reflecting corporate strategies to balance shareholder returns with reinvestment amid market volatility. - Bitcoin's
