Stablecoin Leaders USDT and USDC Lose Ground as Their Dominance Falls to 83%
Tether’s USDT and Circle’s USDC have long stood at the top of the stablecoin sector. For years, these two assets made up nearly the entire market, leaving little space for others. That landscape is now changing. Their combined share is slipping as new competitors, regulatory frameworks, and banks begin reshaping the field.

In brief
- USDT and USDC have seen their market share fall from 91% in March 2024 to 83% currently, signaling growing influence of rival stablecoins.
- These new stablecoins are attracting interest by offering yield to investors, providing viable alternatives to the traditional leaders.
- Major banks are also exploring entry into the stablecoin market through potential consortia, a move that could significantly reshape the sector.
Declining Dominance of USDT and USDC
The global stablecoin market was valued at over $140 billion, with USDT at around $103 billion and USDC at about $29 billion in March 2024, together accounting for 91.6% of the total supply and giving the two coins an almost complete grip on the market.
That dominance has begun to wane. Data from DefiLlama shows that USDT and USDC now account for 83.27% of the stablecoin market share , a decline of more than eight percentage points, signaling a slow but steady erosion of their control. Analyst Nic Carter points out that this downward trend is likely to continue, driven by rising structural and competitive pressures in the market.
New Stablecoins Compete Through Yield
Carter points out that the market now hosts a wider mix of established stablecoins than in earlier cycles. PayPal has released PYUSD, World Liberty introduced USD1, Ethena launched USDe, and Sky brought forward USDS.
Other names are also rising, including Ondo’s USDY, Paxos’ USDG, and Agora’s AUSD. These new projects have begun attracting investors and broadening the overall supply base.
Compared with earlier market cycles, he noted that “there are a lot more credible stablecoins than there were during the last surge, and they collectively have more supply than they did in the prior bull market – even against the backdrop of Tether and Circle continuing to dominate market share and liquidity.”
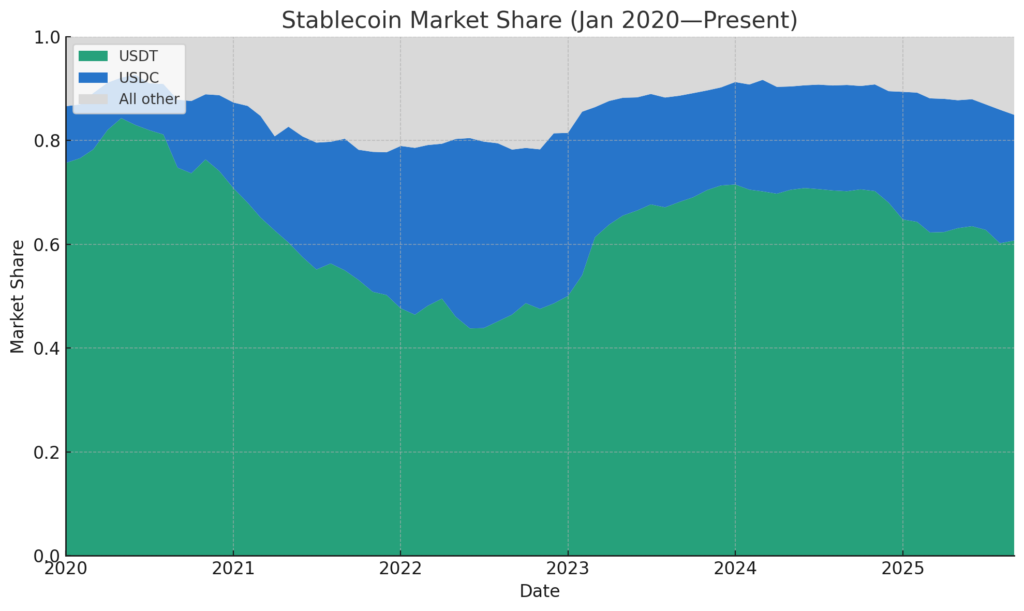 Stablecoin market share over time: dominance of USDT and USDC
Stablecoin market share over time: dominance of USDT and USDC
What separates many of the newcomers is their ability to shift yield back to holders. In contrast, Tether provides no yield, while Circle offers only limited rewards through partners such as Coinbase. This makes newer stablecoins more appealing to holders seeking returns.
While the GENIUS ACT framework formally restricts stablecoin issuers from paying yield directly, it does not stop third-party platforms or intermediaries from offering rewards, often through arrangements with issuers. According to him, this regulatory gap has allowed yield-bearing models to expand, giving new entrants an advantage over established players.
GENIUS doesn’t actually prohibit third-party platforms or intermediaries from paying rewards to stablecoin holders (which are, in turn, paid to the intermediaries by the issuers).
Nic Carter
Stablecoin Competition Set to Grow with Bank Participation
Recent regulatory changes are also reshaping the stablecoin market by allowing banks and other financial institutions to issue their own coins. Carter notes that, while concerns about potential deposit runs persist, major banks are actively exploring entry into the space.
Earlier this year, JPMorgan, Bank of America, Citigroup, and Wells Fargo held preliminary discussions about forming a stablecoin consortium. He explained that “a consortium makes by far the most sense, as no bank individually has the ability to create the necessary distribution for a stablecoin which could compete with Tether.”
The potential participation of banks could significantly expand the market. Carter explains that their entry may overshadow the current $300 billion market and create a new layer of competition for existing stablecoins.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
OG Strategies May Be Hurting Bitcoin’s Momentum

Is FET Nearing a Recovery Phase? This Key Emerging Fractal Suggests So

Core (CORE) Testing Key Resistance – Could This Pattern Trigger an Upside Breakout?

Zcash Halving 2025: Effects on the Market, Investor Reactions, and Tactical Investment Prospects
- Zcash's 2025 halving reduces block rewards by 50%, tightening supply and reinforcing its deflationary model. - The event coincided with a 1,172% price surge, driven by institutional investments and growing shielded transaction adoption. - Institutional demand, including Grayscale and Cypherpunk's ZEC acquisitions, highlights Zcash's strategic value in privacy-focused crypto markets. - Regulatory risks under MiCA and short-term volatility remain concerns, but long-term projections suggest potential for $1

