FOMO, Involution, and the Prisoner's Dilemma: The Psychological Warfare of an On-Chain Trading Competition
Behind the limited rewards lies an infinite game. The essence of trading competitions is a collective prisoner's dilemma—whether to achieve a Nash equilibrium or fall short, this uncertain game further excites traders’ nerves.
Author:CryptoBrand

In the Web3 market of 2025, the narrative is quietly shifting. In addition to the ever-popular Meme, more solid tracks are beginning to emerge, such as RWA tokenization, which is making waves. Data shows that the trading volume of tokenized Pokémon cards alone reached approximately $124 million in August 2025. At the same time, the Web3 infrastructure sector is also accelerating its maturity due to the injection of institutional funds and improvements in technical indicators.
Against this backdrop, liquidity is the lifeline. Whether for emerging protocols or established platforms, trading volume directly affects market attention, token prices, and even survival. Trading competitions, as a powerful tool, have been given new life in the world of Web3.
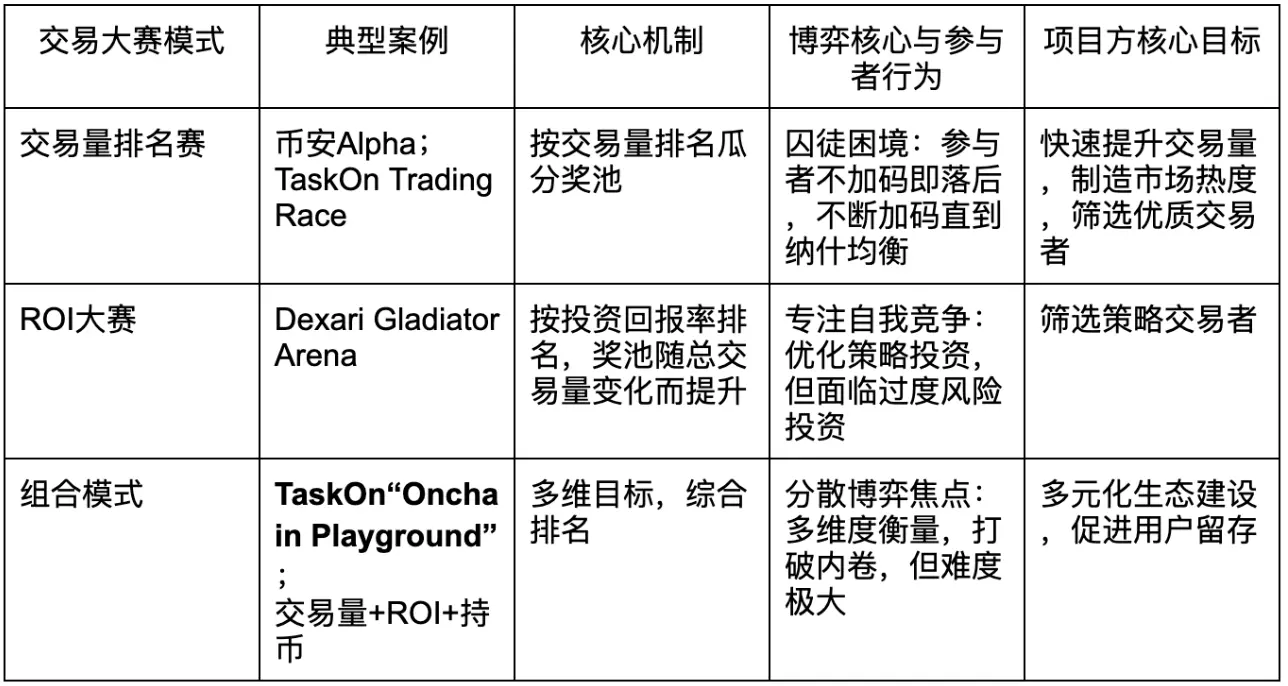
Trading Competitions: Catalysts for Project Growth and Engines for Multi-Party Win-Win
Trading competitions are essentially a carefully designed incentive game, where participants each get what they need, together forming a subtle ecosystem.
1. The Moat of CEX: Binance Alpha Trading Competition
Binance’s Alpha program is a typical CEX approach. The triple incentives of “Alpha Points,” “Ecosystem Competition Rewards,” and “Designated Trading Pair Rewards” achieve a “three-in-one” effect. Massive “off-site traffic” is channeled through trading competitions, boosting the platform’s trading activity and user stickiness, while also bringing valuable initial liquidity and attention to ecosystem projects.
2. The Liquidity Engine of DEX: PancakeSwap’s Trading Competition
Trading competitions can incentivize LPs, attracting users to inject assets into liquidity pools through rewards, thereby increasing the protocol’s TVL and trading depth, reducing users’ trading slippage, and forming a positive cycle.
3. The Clever Bridge of Task Platforms: TaskOn’s Trading Race
Task platforms connect project teams and massive users in the Web3 ecosystem, helping projects with cold starts through diversified tasks. TaskOn’s Trading Race leverages a relatively low reward budget to drive astonishing trading volume. Through the Leaderboard and real-time distribution of reward incentives, it activates participants’ competitive spirit, turning simple trading behavior into a passionate competition.
Nash Equilibrium and the Prisoner’s Dilemma in On-Chain Trading Competitions
Why can trading competitions become the golden finger to activate trading volume? Why does rational analysis ultimately lead to collective “involution”? When many participants are placed in the same arena, there is an addictive game theory mechanism hidden behind the micro-level competition.
Trading competitions are naturally a perfect stage for the prisoner’s dilemma. Each participant faces a choice: to remain restrained or to increase trading? If everyone restrains themselves, collective returns are optimal, but as soon as one person “betrays” and increases their trading, they can easily surpass others. Risk aversion and FOMO emotions drive everyone to keep involuting until the prize is diluted by fees. Eventually, the market tends toward Nash equilibrium—everyone’s input makes their net returns approach the overall minimum, at which point no one is willing to unilaterally change their strategy. This “zero-sum equilibrium” is precisely the state of maximum incentive efficiency that project teams are happy to see.
Practical Deduction: The “Attrition” Game of Binance Alpha Trading Competition
Binance Alpha recently launched a BNB Smart Chain trading competition, where participants compete for a prize pool worth $3.1 million by trading in five independent volume pools: AKE, ARIA, TAKE, BOT, and RICE.
Participants fiercely compete for rankings.Heisenberg, who often participates in Binance Alpha, showed me his trading strategy: “‘Buy at the lowest fee rate, set a 2%-5% sell order, and earn a small price difference while wash trading.” But Kai immediately retorted,“Buy and sell immediately, I lost 1.6U.”
At the end of the competition, the game reaches a fever pitch. “The last day of the previous trading competition was extremely intense; some people suffered tens of U in attrition,” Heisenberg vividly described why it falls into the prisoner’s dilemma: “We’re all betting on when the other will give up. Each time, the advantage of a few hundred U alternates in the rankings, and in the end, all the profits are thrown in and it just stops. Only by staying calm can you make money, but unfortunately, you can’t persuade others, nor can you persuade yourself to accept a loss.”
Also, a reminder to traders: be sure to calculate trading friction and research the token background, because only by making money does participating in trading competitions make sense.
Efficiency and Capital: The Efficiency of TaskOn Trading Race
On the TaskOn platform, aQLS liquidity and trading sprint competitionused a $1,155 prize pool to drive over $300,000 in trading volume.
The Trading Race pagedisplays real-time information on trading volume, total prize pool, and participants, but does not enlarge the Swap entry. Instead, the Leaderboard is placed in the most prominent position. Through changes in rankings and real-time rewards, it provides a public, real-time updated leaderboard. As users’ rankings rise or fall, their competitive psychology and desire to win fluctuate accordingly, which is the biggest source of adrenaline and also stimulates increased trading enthusiasm.
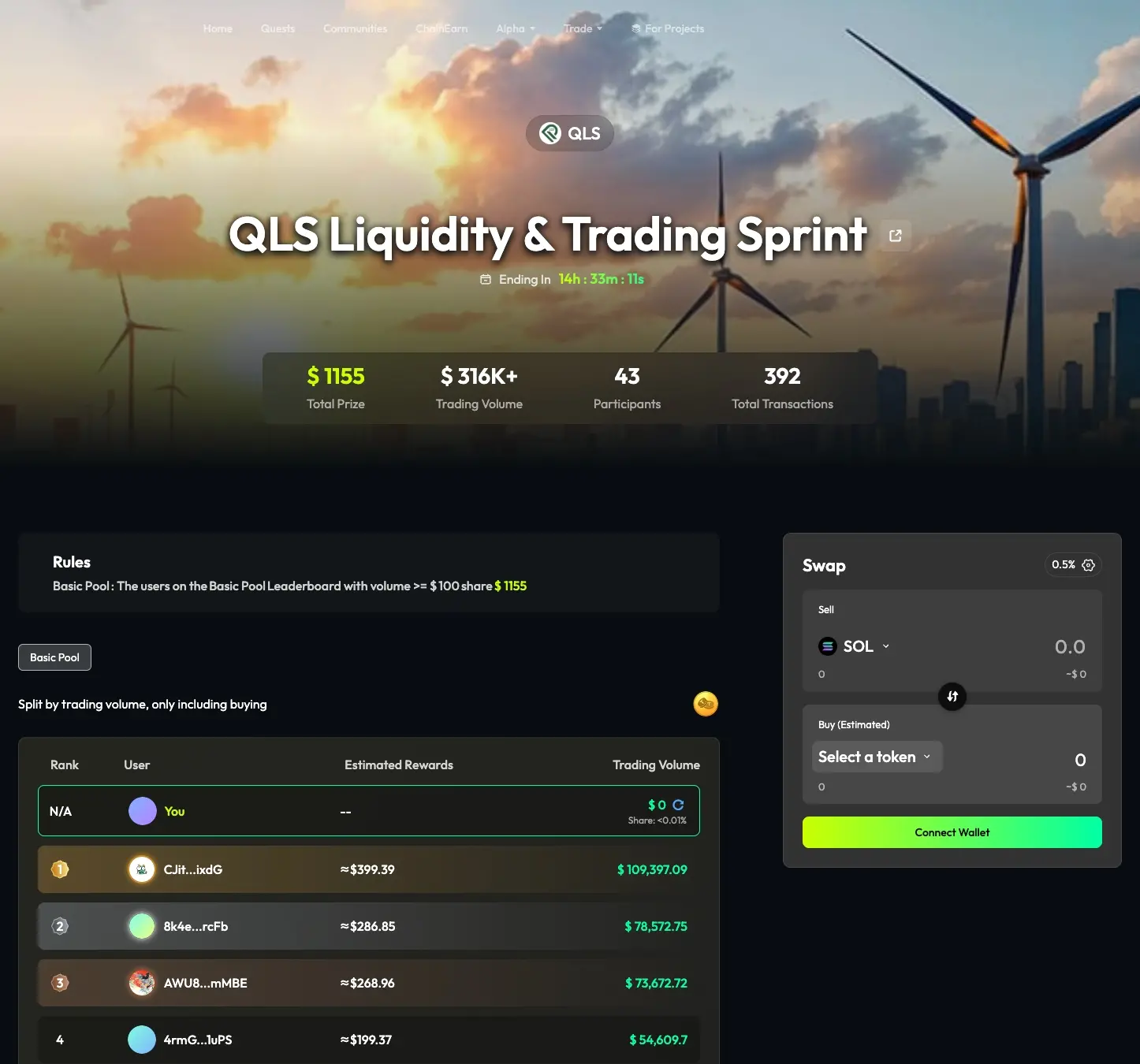
In the white-hot stage of the game, the endowment effect and sunk cost provide deeper psychological interference. Once users achieve a certain ranking through trading, they regard this “temporary ownership” as already theirs. As their ranking drops, risk aversion and sunk costs drive them to “give it another shot” in an attempt to recover “losses.” Sometimes, this competition is not even about rewards, but about honor.
In TaskOn’s Discord community, I saw users asking administrators whether badges related to the Trading Race could be launched. I privately messaged a user named “Bella,” who said, “The journey of large trades is more often a reflection of on-chain honor. Sharing such badges on Twitter is more natural than simply posting trading screenshots.”
Therefore, TaskOn also maintains a balance in rule design. All trading information—users’ trading volume, expected returns—is transparently available, making it easier to calculate the overall cost and to achieve Nash equilibrium. When the generally balanced trading point is calculated and set as the trading baseline, retail investors can more controllably maximize their benefits.
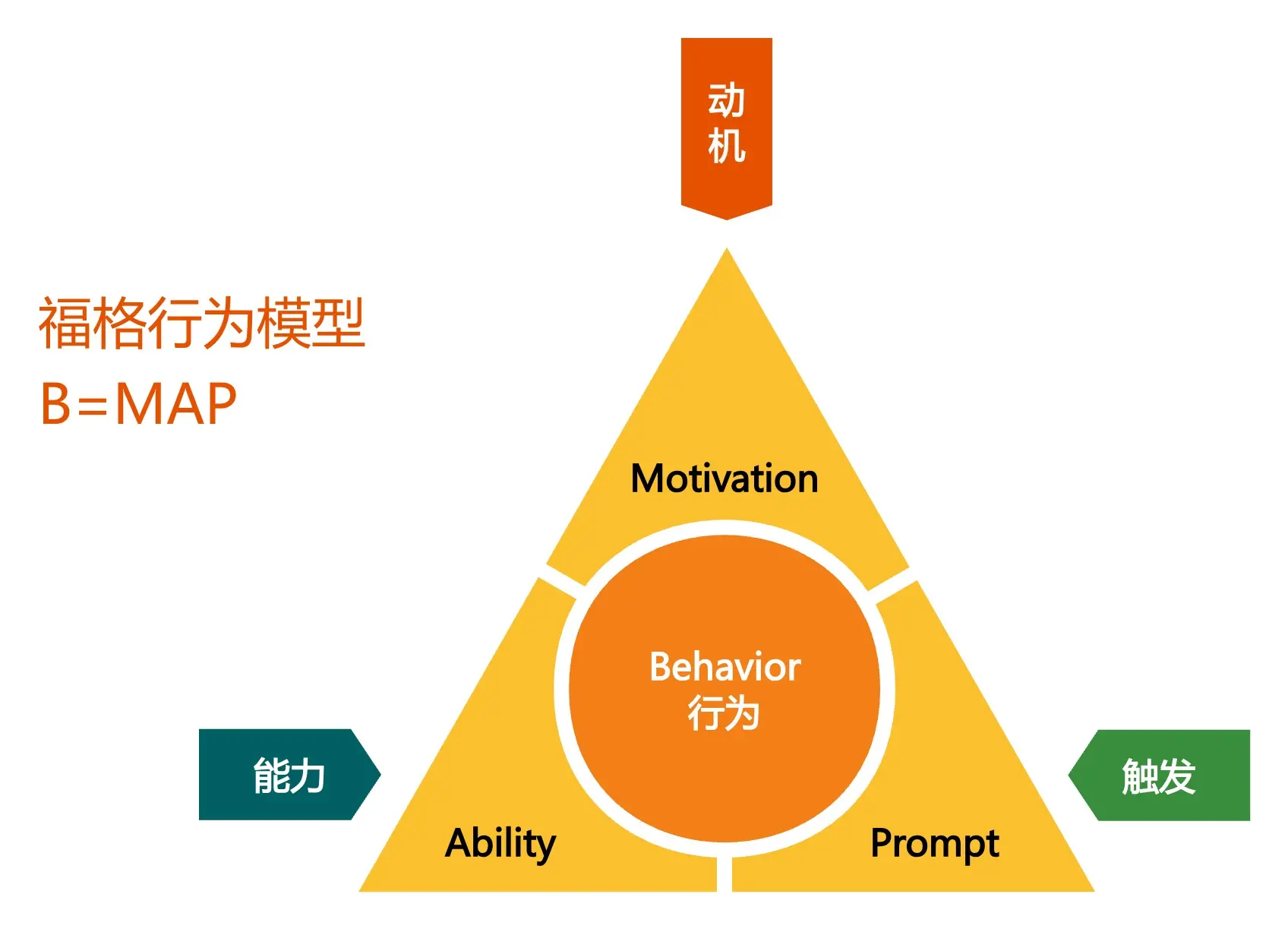
As the Fogg Behavior Model explains: when strong motivation, simplified operational ability, and ubiquitous leaderboard triggers are all present, users’ trading behavior becomes unstoppable, like mercury pouring out.
How to Build a Successful Trading Competition?
The underlying logic of a successful trading competition must first make good use of the hook model—a cycle that makes users “addicted.”
Just like the TaskOn Trading Race we analyzed, the four stages of the hook model turn users from passive participants into active investors:
Trigger: Event announcements, community pushes (external triggers), and FOMO anxiety (internal triggers) start the cycle;
TaskOn’s Trading Race event is promoted on the homepage and widely publicized on Twitter and other channels. Public dynamic returns and FOMO emotions more easily kickstart the flywheel;
Action: Users perform the simplest trading operations;
Variable Reward: The most ingenious part of the hook model: the fluctuation of leaderboard rankings and the uncertainty of rewards constitute variable rewards, continuously stimulating users’ dopamine secretion;
Leaderboard fluctuations and an expected return directly dropping by $100 make the intuitive “loss” more likely to drive users’ trading emotions.
Investment: The time, gas fees, and even emotions users invest increase their sunk costs;
Ultimately, this forms a positive flywheel. Once the flywheel reaches its limit, project teams can build a standardized competition brand around the path of “rules—rewards—competitive atmosphere (leaderboard)—branding,” forming a cycle of positive growth.
The Deep Value and Future Evolution of Trading Competitions
In addition to independent operations by single project teams, trading competitions jointly held by projects within the same ecosystem can better achieve ecosystem empowerment and scale effects in trading volume. As trading dimensions increase, gameplay also becomes more diversified, making users’ trading strategies the main focus of the competition.
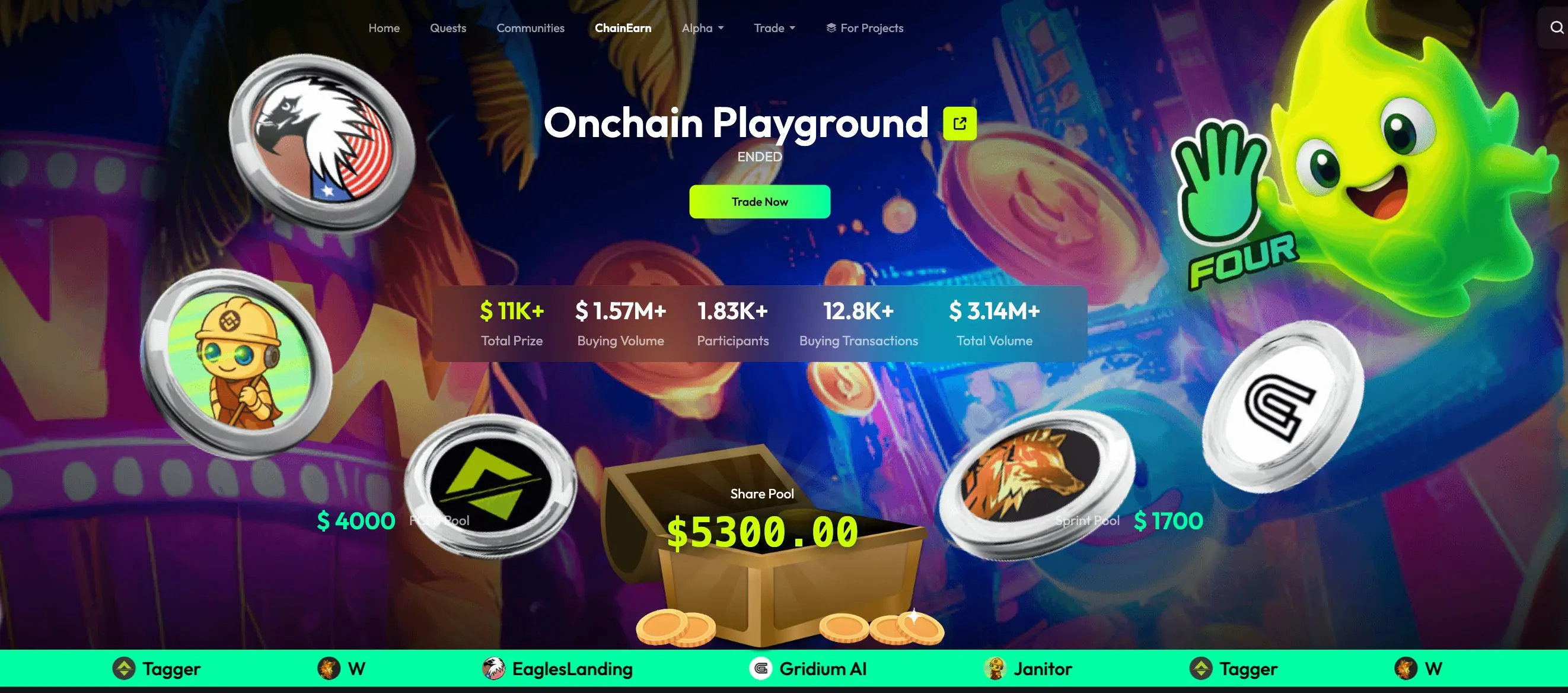
Advanced Case: TaskOn and FourMeme’s “Onchain Playground”
The Meme trading competition “Onchain Playground” jointly launched by TaskOn and FourMeme is a model of this approach. It brings together five popular Meme coins such as $EGL1 and $Janitor, and designs a sophisticated “three-dimensional” flywheel gameplay, elevating the competition from simple involution to a strategic dimension:
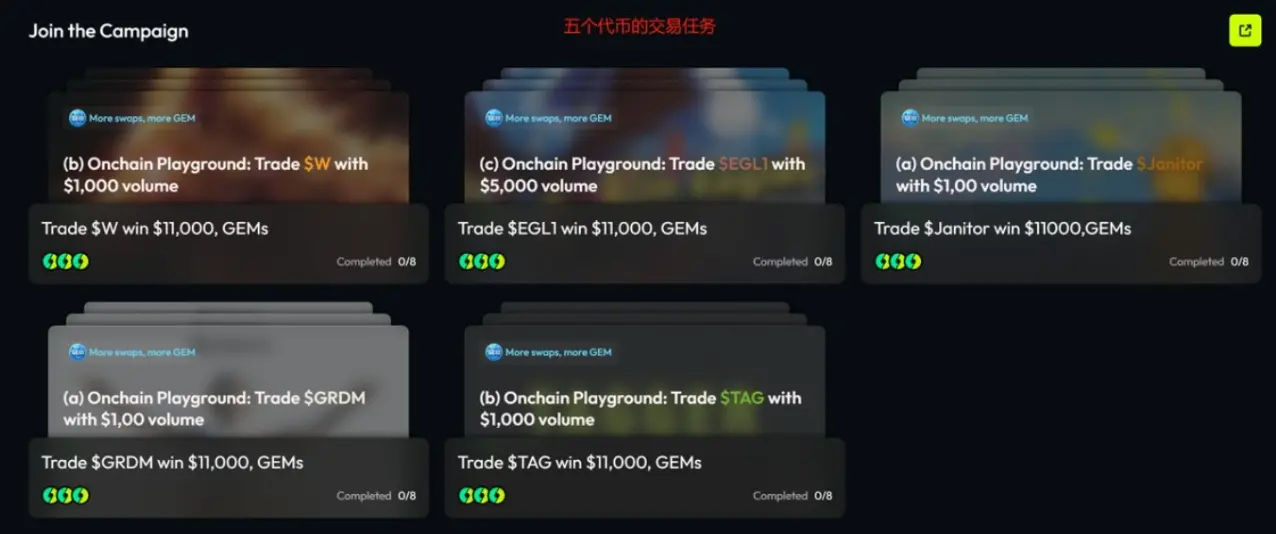
FCFS Pool: Users complete trading tasks for their preferred projects to share a $4,000 base prize pool and receive platform GEMs rewards.
Share Pool: Users must consider multiple “Task Collections” and compete for the total trading volume leaderboard to share a $5,300 prize pool. This pool grows dynamically with total trading volume, breaking the upper limit of returns and incentivizing core players to keep investing.
Sprint Pool: This activates the value of GEMs gameplay, with the final $1,700 sprint pool divided based on the number of GEMs. At this point, GEMs become the sole metric for measuring returns.
The ingenuity of this mechanism lies in successfully implanting the core strategic question of “how to efficiently obtain GEMs” among users. Users not only compete in trading volume but also balance their energy allocation among different tasks, thinking about optimal strategies to maximize benefits from all three prize pools. It also demonstrates the potential of joint competitions—through the three-dimensional design of the basic game layer, strategy competition layer, and resource allocation layer, the competition is elevated from a simple trading volume contest to a strategic game dimension. Ultimately, the total trading volume exceeded $3 million, with over 1,000 users participating in the trading contest.
For project teams, trading competitionsare a lever to kickstart growth;for users, they are also an excellent trading testing ground. The future model of trading competitions can be even more diversified.
In fact, future trading competitions can develop toward Hold Token competitions, combined with veToken models, ve(3,3) models, etc.,transforming short-term incentives into long-term protocol binding, revenue distribution, and weight boosting. This better fits the needs of the Web3 ecosystem.
On-chain trading competitions are a micro-laboratory that perfectly combines human game theory, economic incentives, and cryptographic technology. They clearly demonstrate that, under reasonable rule design, even though individual rational decisions may fall into the “prisoner’s dilemma,” ultimately, in the “Nash equilibrium,” the entire ecosystem can be driven toward a more active, stable, and prosperous direction.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Crypto, TradFi sentiment improves: Will Bitcoin traders clear shorts above $93K?
Bitcoin catches a bid, but data shows pro traders skeptical of rally above $92K

Trending news
MoreBitget Daily Digest (Dec. 9)|Michael Saylor is promoting a Bitcoin-backed banking system to governments; the CFTC has launched a digital asset pilot program allowing BTC, ETH, and USDC to be used as collateral
[English Thread] Wake-up Call and Review for the Crypto Industry in 2025: Where Is the Direction of the Next Cycle?
