Financial Black Hole: Stablecoins Are Devouring Banks
Stablecoins, acting as "narrow banks," are quietly absorbing liquidity and reshaping the global financial architecture.
Original Title: Stablecoins, Narrow Banking, and the Liquidity Blackhole
Original Author: @0x_Arcana
Translation: Peggy, BlockBeats
Editor's Note: As the global financial system gradually digitizes, stablecoins are quietly becoming an undeniable force. They do not belong to banks, money market funds, or traditional payment systems, yet they are reshaping the flow of the US dollar, challenging the transmission mechanism of monetary policy, and sparking a profound discussion about the "financial order."
This article starts with the historical evolution of "narrow banking," delving into how stablecoins replicate this model on-chain and, through the "liquidity blackhole effect," impact the US Treasury market and global financial liquidity. Against a backdrop where policy regulation remains unclear, the non-cyclical expansion, systemic risk, and macro impact of stablecoins are becoming new issues that the financial world cannot ignore.
The following is the original text:
Stablecoins Revive "Narrow Banking"
For over a century, monetary reformers have repeatedly proposed various concepts of "narrow banking": financial institutions that issue money but do not provide credit. From the Chicago Plan of the 1930s to the modern proposal of The Narrow Bank (TNB), the core idea is to prevent bank runs and systemic risk by requiring money issuers to hold only safe, highly liquid assets (such as government bonds).
However, regulators have consistently refused to allow narrow banks to materialize.
Why? Because although theoretically safe, narrow banks would disrupt the core of the modern banking system—the credit creation mechanism. They would siphon deposits from commercial banks, hoard risk-free collateral, and break the link between short-term liabilities and productive lending.
Ironically, the crypto industry has now "revived" the narrow banking model in the form of fiat-backed stablecoins. The behavior of stablecoins almost completely mirrors the liabilities of narrow banks: they are fully collateralized, instantly redeemable, and primarily backed by US Treasuries.
After a wave of bank failures during the Great Depression, economists from the Chicago School proposed a vision: to completely separate money creation from credit risk. According to the 1933 "Chicago Plan," banks would be required to hold 100% reserves against demand deposits, and loans could only be made from time deposits or equity, not from deposits used for payments.
The original intent of this idea was to eliminate bank runs and reduce instability in the financial system. If banks cannot lend out deposits, they will not collapse due to liquidity mismatches.
In recent years, this concept has re-emerged in the form of "narrow banking." Narrow banks accept deposits but only invest in safe, short-term government securities, such as Treasury bills or Federal Reserve reserves. A recent example is The Narrow Bank (TNB), which applied in 2018 to access the Federal Reserve's Interest on Excess Reserves (IOER) but was rejected. The Fed worried that TNB would become a risk-free, high-yield deposit alternative, thereby "weakening the transmission mechanism of monetary policy."
What regulators are truly concerned about is: if narrow banks succeed, they could weaken the commercial banking system by drawing deposits away from traditional banks and hoarding safe collateral. Essentially, narrow banks create money-like instruments without supporting the credit intermediation function.
My personal "conspiracy theory" is that the modern banking system is essentially a leveraged illusion, operating on the premise that no one tries to "find an exit." Narrow banks directly threaten this model. But upon closer inspection, this is not so much a conspiracy—it simply exposes the fragility of the existing system.
Central banks do not directly print money; instead, they regulate indirectly through commercial banks: encouraging or restricting lending, providing support during crises, and maintaining sovereign debt liquidity by injecting reserves. In exchange, commercial banks receive zero-cost liquidity, regulatory leniency, and implicit bailout promises during crises. In this structure, traditional commercial banks are not neutral market participants but tools for state intervention in the economy.
Now, imagine a bank saying: "We don't want leverage; we just want to provide users with safe money backed 1:1 by Treasuries or Federal Reserve reserves." This would render the existing fractional reserve banking model obsolete and directly threaten the current system.
The Fed's rejection of TNB's master account application is a manifestation of this threat. The problem is not that TNB might fail, but that it might actually succeed. If people can obtain a currency that is always liquid, risk-free, and earns interest, why would they keep their money in traditional banks?
This is precisely where stablecoins come into play.
Fiat-backed stablecoins almost perfectly replicate the narrow banking model: issuing digital liabilities redeemable for dollars and backing these liabilities 1:1 with safe, liquid off-chain reserves. Like narrow banks, stablecoin issuers do not use reserve funds for lending. While issuers like Tether currently do not pay interest to users, this is beyond the scope of this article. The focus here is the role of stablecoins in the modern monetary structure.
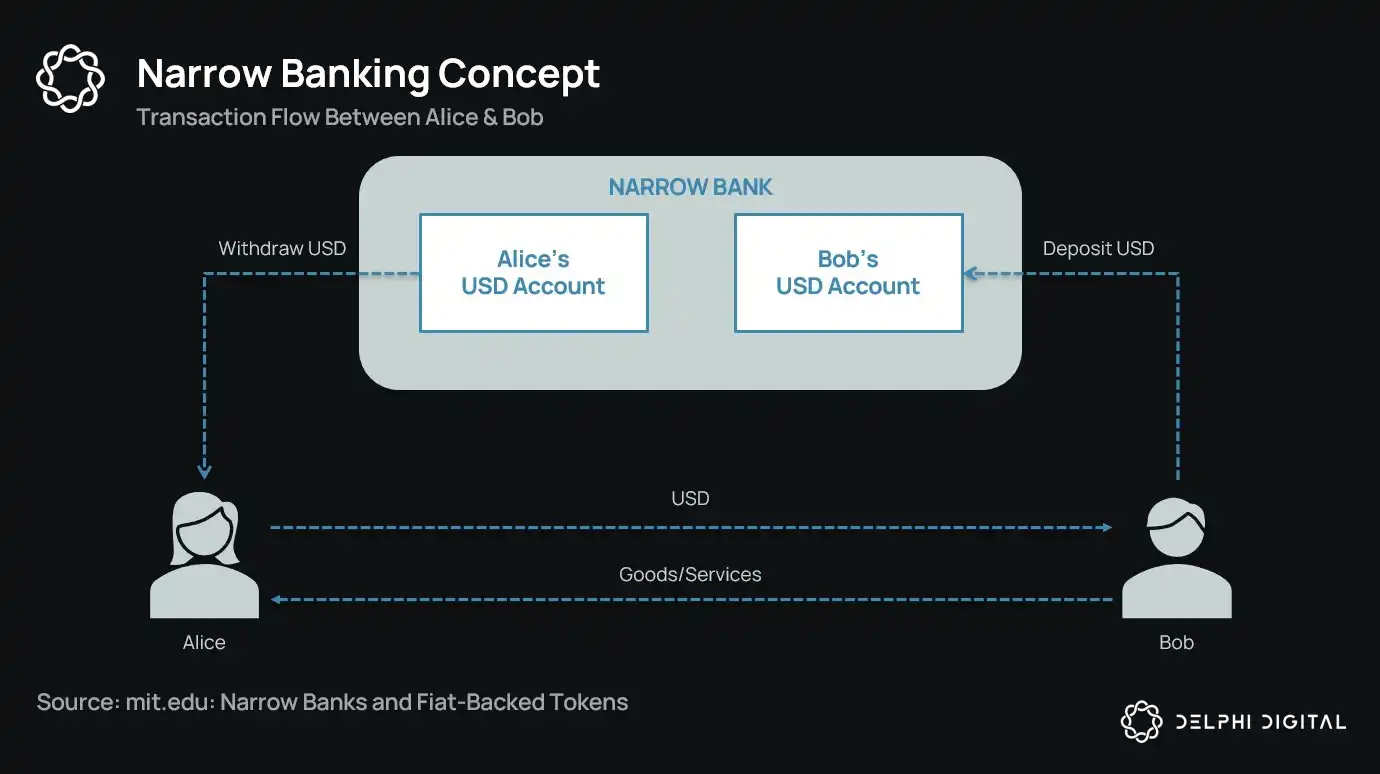
The assets are risk-free, the liabilities are instantly redeemable, possessing the attributes of face-value currency; there is no credit creation, no maturity mismatch, and no leverage.
And while narrow banks have been "strangled" at birth by regulators, stablecoins have not faced similar restrictions. Many stablecoin issuers operate outside the traditional banking system, and especially in high-inflation countries and emerging markets, demand for stablecoins continues to grow—these regions often have difficulty accessing US dollar banking services.
From this perspective, stablecoins have evolved into a kind of "digitally native Eurodollar," circulating outside the US banking system.
But this also raises a key question: When stablecoins absorb enough US Treasuries, what impact will this have on systemic liquidity?
Liquidity Blackhole Thesis
As stablecoins grow in scale, they increasingly resemble global liquidity "islands": absorbing dollar inflows while locking safe collateral in a closed loop that cannot re-enter the traditional financial cycle.
This could lead to a "liquidity blackhole" in the US Treasury market—where a large amount of Treasuries are absorbed by the stablecoin system but cannot circulate in the traditional interbank market, thereby affecting the overall liquidity supply of the financial system.
Stablecoin issuers are long-term net buyers of short-term US Treasuries. For every dollar of stablecoin issued, there must be an equivalent asset on the balance sheet—usually Treasury bills or reverse repo positions. But unlike traditional banks, stablecoin issuers do not sell these Treasuries for lending or shift them into risk assets.
As long as stablecoins remain in circulation, their reserves must be continuously held. Redemption only occurs when users exit the stablecoin system, which is very rare, as on-chain users typically just swap between different tokens or use stablecoins as long-term cash equivalents.
This makes stablecoin issuers a one-way liquidity "blackhole": they absorb Treasuries but rarely release them. When these Treasuries are locked in custodial reserve accounts, they exit the traditional collateral cycle—they cannot be re-hypothecated or used in the repo market, effectively being removed from the monetary circulation system.
This creates a "sterilization effect." Just as the Fed's quantitative tightening (QT) tightens liquidity by removing high-quality collateral, stablecoins are doing the same—but without any policy coordination or macroeconomic objectives.
Even more potentially disruptive is the concept of "shadow quantitative tightening" (Shadow QT) and a persistent feedback loop. It is non-cyclical, does not adjust according to macroeconomic conditions, but instead expands as demand for stablecoins grows. Moreover, since many stablecoin reserves are held offshore in jurisdictions outside the US with lower transparency, regulatory visibility and coordination become even more challenging.
Worse still, this mechanism can become pro-cyclical in certain situations. When market risk aversion rises, demand for on-chain dollars often increases, driving up stablecoin issuance and further pulling more US Treasuries out of the market—precisely when the market most needs liquidity, the blackhole effect intensifies.
Although the scale of stablecoins is still much smaller compared to the Fed's quantitative tightening (QT), their mechanism is highly similar, and the macro impact is much the same: fewer Treasuries circulating in the market; tighter liquidity; marginal upward pressure on interest rates.
Moreover, this growth trend has not slowed down; on the contrary, it has accelerated significantly in recent years.
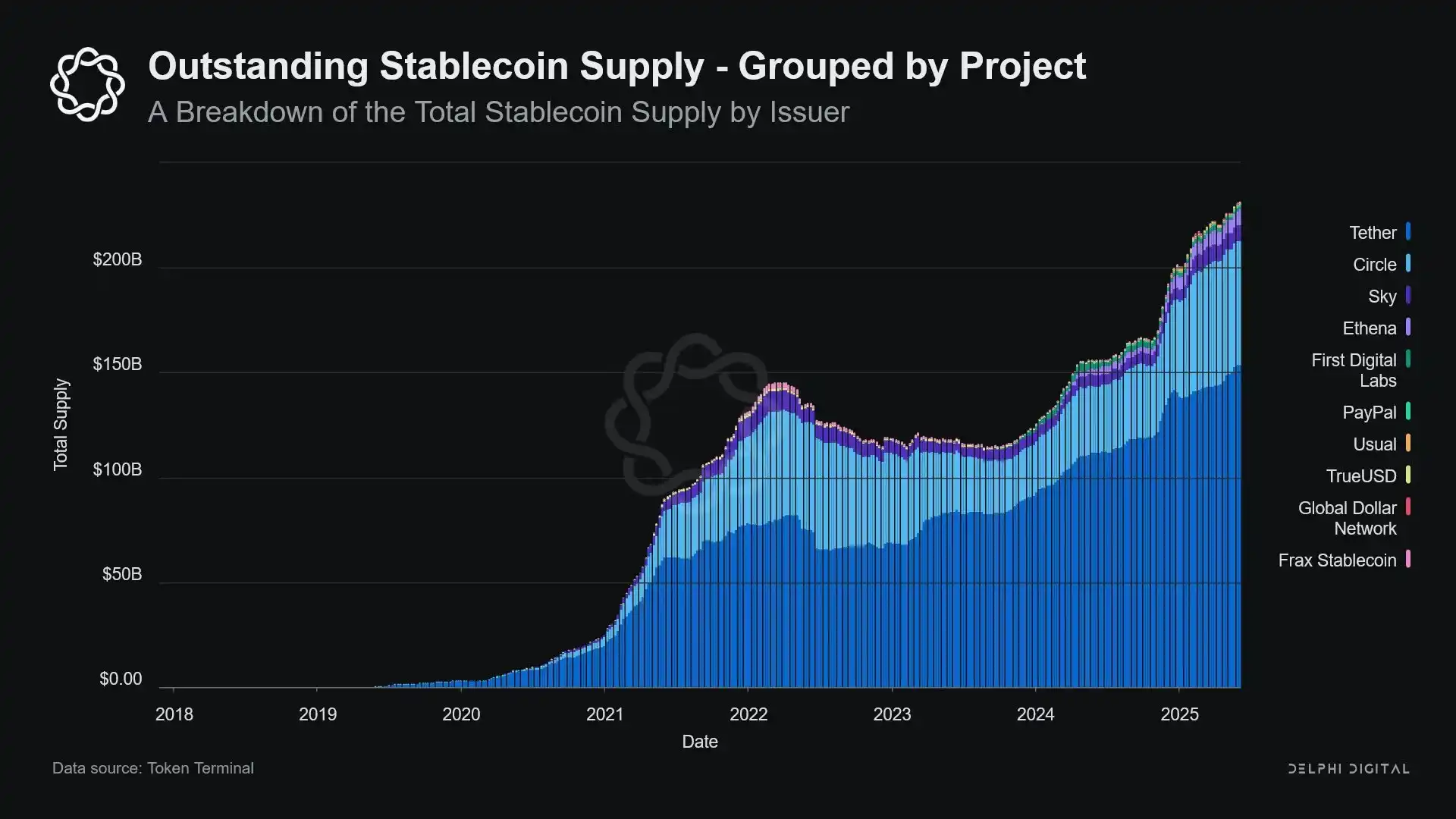
Policy Tension and Systemic Risk
Stablecoins occupy a unique intersection: they are neither banks, nor money market funds, nor traditional payment service providers. This identity ambiguity creates structural tension for policymakers: too small to be regulated as systemic risk; too important to be simply banned; too useful, yet too dangerous to develop freely without regulation.
A key function of traditional banks is to transmit monetary policy to the real economy. When the Fed raises rates, bank credit tightens, deposit rates adjust, and lending conditions change. But stablecoin issuers do not lend, so they cannot transmit interest rate changes to the broader credit market. Instead, they absorb high-yield US Treasuries, do not provide credit or investment products, and many stablecoins do not even pay interest to holders.
The Fed's refusal to grant The Narrow Bank (TNB) access to a master account was not due to credit risk, but out of concern for financial disintermediation. The Fed worries that if a risk-free bank offers interest-bearing accounts backed by reserves, it would attract large amounts of funds out of commercial banks, potentially undermining the banking system, squeezing credit space, and concentrating monetary power in a "liquidity sterilization vault."
The systemic risk brought by stablecoins is similar—but this time, they do not even need the Fed's approval.
Moreover, financial disintermediation is not the only risk. Even if stablecoins do not offer yields, there is still "run risk": if the market loses confidence in reserve quality or regulatory stance, it could trigger a wave of redemptions. In such cases, issuers may be forced to sell Treasuries under market pressure, similar to the 2008 money market fund crisis or the 2022 UK LDI crisis.
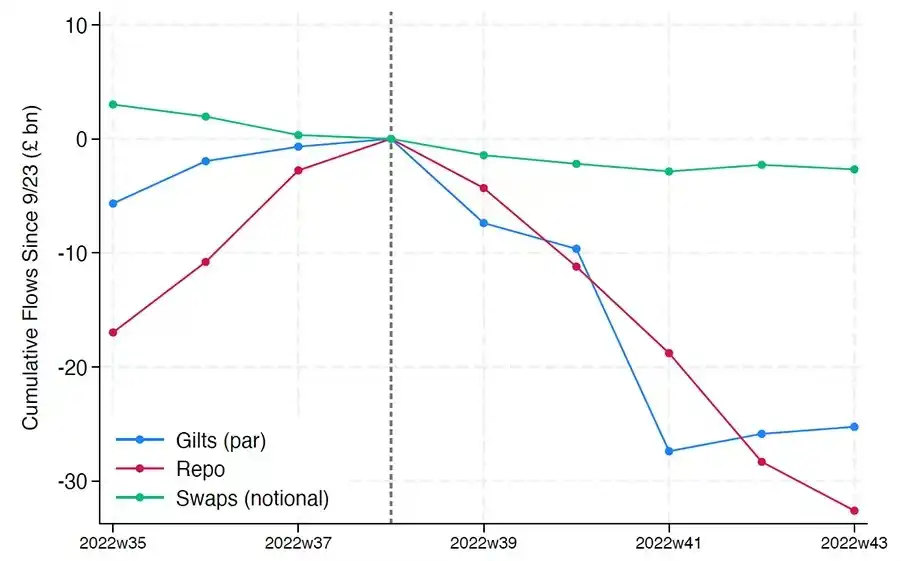
Unlike banks, stablecoin issuers do not have a "lender of last resort." Their shadow banking nature means they can quickly grow into a systemic role, but can also collapse just as rapidly.
However, just like bitcoin, there is also a small portion of "lost seed phrase" scenarios. In the context of stablecoins, this means that some funds will be permanently locked in US Treasuries, unrecoverable, effectively becoming a blackhole of liquidity.
The initial issuance of stablecoins was just a marginal financial product in crypto trading venues, but now it has become a main channel for dollar liquidity, spanning exchanges, DeFi protocols, and even extending to cross-border remittances and global commercial payments. Stablecoins are no longer marginal infrastructure; they are gradually becoming the underlying architecture for dollar transactions outside the banking system.
Their growth is "sterilizing" collateral, locking safe assets into cold storage reserves. This is a form of balance sheet contraction occurring outside central bank control—a kind of "ambient quantitative tightening" (ambient QT).
And while policymakers and the traditional banking system are still striving to maintain the old order, stablecoins have quietly begun to reshape it.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Massive $577M ETH Long Position: Bitcoin OG Doubles Down on Ethereum Bet
UK Treasury Finalizes Cryptoasset Rules, Setting 2027 Start Date for Full Oversight
'Built for This': Michael Saylor Denies Panic Amid Bitcoin's Price Roller Coaster
Dogecoin Forms Crucial Support at $0.074: Big Price Move Ahead?
